The excretory system is a part of a live organism's body that disposes of waste.
Organs of the human excretory system include:
- A couple of kidneys
- A ureter is a tube that connects the kidneys to the bladder.
- The bladder of the urinary system
- A urethra is a tube that connects the bladder to the urine
A couple of kidneys
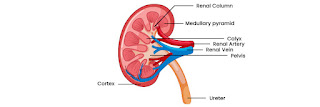
Each person is born with two kidneys. On either side of the backbone are the kidneys, which are bean-shaped organs. The kidneys are protected by the ribs and back muscles. Each adult human kidney measures 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width, and weighs 120-170 grammes.
Renal Capsule is a type of capsule that is used to treat kidney problems
The fibrous tissue that surrounds the kidney is referred to as the renal capsule. The renal cortex and renal medulla are two zones on the interior of the kidney. The outer layer of the kidney is the renal cortex, while the inner layer is the renal medulla. Renal columns run between the medullary area and the renal cortex. These renal columns are also referred to as Bertin columns or Bertin columns.
Nephrons
The working units of the kidney are nephrons, which create urine while eliminating waste and excess substances from the blood. There are around 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney.
The renal tubule and the renal corpuscle are the two elements of a nephron.
Henle Loop
The Henle loop, which has an ascending and descending limb, is the next component of the tubule. As a distal convoluted tubule, the ascending loop continues. The connecting tubule connects the distal convoluted tubule to the collecting ducts. Urine is the fluid that reaches the collecting ducts.
Tag - Class 10 Science; CBSE online class 10 science; online classes for school; online class 10 science
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you we will contact ASAP.