BODMAS RULE & BODMAS FULL FORM AND EXAMPLES
BODMAS RULE, FULL FORMAT, AND EXAMPLES – In mathematics, the BODMAS Rule is the series that is used to solve mathematical equations and operations. An order of mathematical operations is what it's called. This rule applies when more than one mathematical operation is used in a single operation.
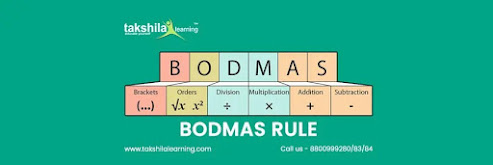
The BODMAS Rule makes it easy for kids to solve math problems. Brackets, Orders, Division/Multiplication, and Addition/Subtraction are all abbreviations for BODMAS Full Form.
Add, subtract, multiply, divide, squaring, and other “mathematical operations” are examples. If the value in a mathematical expression isn't a number, it's most likely an operation.
When confronted with a mathematical problem containing multiple operations, the operations will be solved in the order specified by the BODMAS Law.
BODMAS FULL FORM:
B – Bracket () {} []
O- Order of power and roots or exponents
D- Divide
M- Multiply
A- Addition
S- Subtraction
Each and every letter of the word BODMAS contains significant importance to comprehend its significance. So to have a superior comprehension of what is called BODMAS, we will separate it into its constituent letters
B – This letter represents the term ‘section’ In the word BODMAS and it is available at the very beginning of the word in light of the fact that while playing out any scientific activity, the arrangement of the section should be discovered first.
O – This letter represents the signifying’ request’ which can be viewed as an umbrella term since it contains powers, square roots, and so forth.
D – This letter is in the word BODMAS to cause us to comprehend the request for use of a division activity.
M –Just like division, Multiplication is likewise an extremely fundamental and regular numerical activity, which here in the word BODMAS is appeared by the letter M.
A – Here in the word BODMAS RULE & BODMAS FULL FORM AND EXAMPLES ‘An’ is utilized to allude to the scientific activity ‘expansion,’ which has its request after the duplication activity.
S – ‘S’ is utilized in this word to allude to the scientific activity deduction’ which should be comprehended finally while fathoming a condition or articulation utilizing the BODMAS hypothesis.
For instance BODMAS Examples :
125×56+60÷2=?
In this expression, the BODMAS rule comes for help. Here, as per the BODMAS rule, first, we have to perform division, followed by Multiplication and afterward addition, which gives the right answer, i.e., 7030.
12+10-5+7
We know addition and subtraction works equally and the order of calculation will be done from left to right.
Solution:
12+10=22
22-5=17
17+7=24
x + (y + z) = x + y + z
Rule – Open the bracket and add the terms
x – (y + Z) = x – y – z
Rule – Open the bracket and multiply the negative sign with each term inside the bracket. (All positive terms will be negative and vice-versa)
To More Know About Bodmas Rule and Order of Operation
Must Read: Class 6th Science – Motion and Measurement of Distance
Takshila Learning provides animated learning modules for CBSE online classes for Class 6. You can Learn with our animated video lectures and watch our online recorded lectures at your convenience understand, learn and practice all concepts of Maths and other subjects. To know more register with us at www.takshilalearning.com. We also provide NCERT SOLUTIONS for Class 6 – 12.
Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you we will contact ASAP.