Integers - Definition and Examples - Class 7 Maths
Definition of an integer: The word "integer" signifies "total" or "whole." Integers are comparable to whole numbers, with the exception that they can contain negative values.
An integer is a number without a decimal or fractional element that comes from the set of negative and positive numbers that includes zero.
Examples of integers
-2, 10, 5, 800, and 1470 are examples of integers. Z represents a set of integers, which consists of:
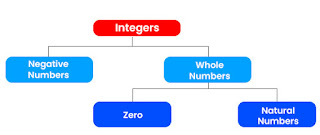
There are three types of integers:
Zero (0): There is no positive (or negative) integer for zero. As a result, zero is a neutral number, meaning it has no sign.
Natural Numbers (Positive Integers): Positive integers are natural numbers (also referred to as counting numbers). The denotation for these integers is Z+. The direction on the number line where positive integers lie is on the right side of 0.
Negative Integers (Natural Numbers' Additive Inverse): Negative integers are the inverse of natural numbers. The denotation for these integers is Z–. The direction on the number line where negative integers lie is on the left side of 0.
For instance, -1, -2, -3, -4, -5......
Number Line Representation — Just like other numbers, integers can be represented on a number line.
Using a Number Line to Display Integers
When arranging integers on a number line, keep the following in mind:
- The right horizontal side's number is always greater than the left horizontal side's number.
- The centre is kept at zero, which has no positive or negative value.
- Positive numbers are placed on the right side of 0 since they are larger than '0.'
- Because negative numbers are smaller than zero, they are positioned to the left of zero.
Click to know for Class 7 - Addition and subtraction of integers

Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you we will contact ASAP.